Christian Woerz
The Eventloop in JavaScript - How does it work?
#1about 4 minutes
Differentiating between a JavaScript engine and a runtime
A JavaScript engine implements the ECMAScript standard, while a runtime adds extra functionality like Web APIs and the event loop.
#2about 2 minutes
Understanding why JavaScript needs an event loop
JavaScript's single-threaded nature can block the UI, so the event loop is necessary to handle asynchronous operations without freezing the application.
#3about 7 minutes
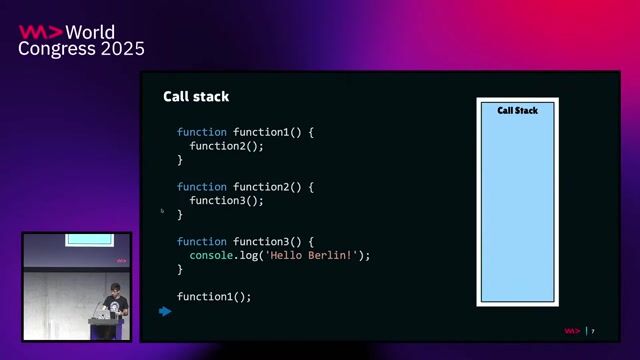
Exploring the core components of a JavaScript runtime
A runtime consists of a call stack for synchronous code, Web APIs for browser or Node features, and separate queues for microtasks and macrotasks.
#4about 2 minutes
How the event loop prioritizes and executes tasks
The event loop continuously checks if the call stack is empty, then processes all available microtasks before handling a single macrotask.
#5about 4 minutes
Demonstrating setTimeout and the macro task queue
Code example shows how `setTimeout` with a zero delay is placed in the macrotask queue and executed only after the synchronous call stack is clear.
#6about 2 minutes
Prioritizing promises with the micro task queue
A resolved promise is handled as a microtask, which is always executed before macrotasks like `setTimeout` when the call stack is empty.
#7about 3 minutes
How network latency affects promise execution order
Using `fetch`, this example shows that a promise is only added to the microtask queue upon resolution, so a slow network request can execute after a faster macrotask.
#8about 3 minutes
Starving the macro task queue with micro tasks
A recursive `queueMicrotask` call demonstrates how continuously adding microtasks can prevent the event loop from ever processing the macrotask queue.
#9about 2 minutes
Final recap of the event loop's execution order
The event loop prioritizes the call stack first, then the entire microtask queue, and finally a single task from the macrotask queue.
Related jobs
Jobs that call for the skills explored in this talk.
Technoly GmbH
Berlin, Germany
Senior
JavaScript
Angular
+1
zeb consulting
Frankfurt am Main, Germany
Junior
Intermediate
JavaScript
HTML
+1
Matching moments
05:24 MIN
Demystifying asynchronous execution with the event loop
Multithreading in Javascript: A guide to Web Workers

05:57 MIN
Visualizing the JavaScript event loop and call stack
JavaScript the Grumpy Parts

04:53 MIN
The four pillars of high-performance JavaScript
Things I learned while writing high-performance JavaScript applications
08:07 MIN
Exploring modern JavaScript performance and new CSS features
WeAreDevelopers LIVE – AI, Freelancing, Keeping Up with Tech and More

03:03 MIN
The origin and design philosophy of JavaScript
JavaScript the Grumpy Parts
03:46 MIN
Overcoming thread limitations with event-driven programming
Concurrency in Python

12:05 MIN
Understanding the fundamentals of event-driven systems
Event Messaging and Streaming with Apache Pulsar

06:05 MIN
Optimizing code by understanding the V8 runtime
Things I learned while writing high-performance JavaScript applications
Featured Partners
Related Videos
 14:44
14:44Catching up on the basics you don't really need that much code
Chris Heilmann
 46:08
46:08JavaScript the Grumpy Parts
Rob Richardson
 27:27
27:27Things I learned while writing high-performance JavaScript applications
Michele Riva
 46:46
46:46The Lean Web
Chris Ferdinandi
 32:54
32:54Beats in the Browser: Coding Music with JavaScript
Rowdy Rabouw
 53:45
53:45Leveraging Server-Sent Events (SSE) for Efficient Data Streaming in UI Development
Rainer Stropek
 40:24
40:24Snappy UI needs no Single-Page Application
Clemens Helm
 52:01
52:01Unleash your web skills on native!
Rowdy Rabouw
Related Articles
View all articles



From learning to earning
Jobs that call for the skills explored in this talk.

Code Healers LLC
Hinesville, United States of America
Remote
€40-50K
Intermediate
Senior
PHP
.NET
React
+2


United Kingdom - 2 minutes ago
Intermediate
API
GIT
Azure
React
Python
+6

Live Wire
Python
Unreal Engine


Frontier Resourcing
Charing Cross, United Kingdom
£50-80K
GIT
React
Vue.js
Node.js
+4


