Philippe De Ryck
Architecting API Security
#1about 2 minutes
The urgent need for API security from day one
Recent studies show widespread vulnerabilities like hard-coded keys and authorization failures, highlighting the necessity of designing for security from the start.
#2about 1 minute
Focusing on secure architecture over just code
The OWASP API Security Top 10 reveals that many critical risks, like broken authorization, are best addressed through architectural design rather than just secure coding practices.
#3about 2 minutes
A typical API architecture overview
A common API architecture consists of clients, an API gateway acting as a single entry point, and various backend APIs or microservices handling specific responsibilities.
#4about 6 minutes
Why perimeter security is no longer enough
A compromised internal service, such as a vulnerable image processor, can breach the entire trusted zone, demonstrating that a single perimeter defense is insufficient.
#5about 5 minutes
Using compartmentalization for defense-in-depth
By isolating high-risk services like image processors into separate trust zones, you can contain the damage from a potential breach as part of a defense-in-depth strategy.
#6about 3 minutes
Isolating both untrusted and sensitive services
Compartmentalization applies both to sandboxing untrusted components and to creating secure enclaves for highly sensitive services like authentication or payments.
#7about 5 minutes
Authenticating internal API-to-API calls
To prevent a compromised internal service from moving laterally, enforce authentication between all internal APIs and define strict policies on which services can communicate.
#8about 5 minutes
Propagating user context to internal APIs
Internal services need user context to make authorization decisions, which can be achieved by forwarding the user's authentication state from the gateway via a token relay.
#9about 4 minutes
Using reference tokens instead of raw JWTs
To avoid exposing large or sensitive JWTs to clients, an API gateway can issue a small, opaque reference token and translate it back to the full JWT for internal API calls.
#10about 2 minutes
Following JWT security best practices
JSON Web Tokens are not a complete security solution and require careful implementation to avoid common pitfalls related to signature validation, algorithm choice, and revocation.
#11about 2 minutes
Key architectural takeaways for API security
Improve your API security by planning for compromise, choosing simple and robust solutions, and using the API gateway to shield internal implementation details from clients.
Related jobs
Jobs that call for the skills explored in this talk.
IGEL Technology GmbH
Bremen, Germany
Senior
Java
IT Security
Bitpanda
Vienna, Austria
Senior
TypeScript
Angular
+3
zeb consulting
Frankfurt am Main, Germany
Remote
Junior
Intermediate
Senior
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Cloud Architecture
+1
Matching moments
01:33 MIN
Essential security measures for protecting public APIs
Security Pitfalls for Software Engineers

05:12 MIN
Securing APIs against broken authentication flaws
Bullet-Proof APIs: The OWASP API Security Top Ten
01:25 MIN
Designing a secure API using protected URL zones
Full-stack role-based authorization in 45 minutes
01:32 MIN
A summary of APIs for multi-layered security
No More Post-its: Boost your login security with APIs

03:39 MIN
Designing APIs for AI consumption and built-in security
Lessons learned from observing a billion API requests
02:36 MIN
Securing APIs with JWT, RBAC, and CORS
API = Some REST and HTTP, right? RIGHT?!

03:50 MIN
Leveraging APIs as a tool for clean architecture
The Great API Debate: REST, GraphQL, or gRPC?
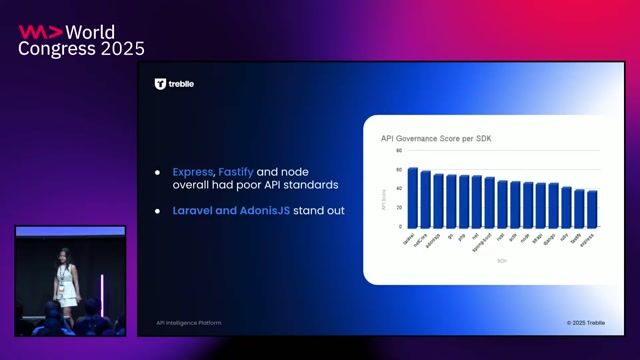
02:34 MIN
Why opinionated frameworks lead to more secure APIs
Lessons learned from observing a billion API requests
Featured Partners
Related Videos
 26:59
26:59Security in modern Web Applications - OWASP to the rescue!
Jakub Andrzejewski
 27:36
27:36Unleashing the Power of Developers: Why Cybersecurity is the Missing Piece?!?
Tino Sokic
 25:46
25:46Bullet-Proof APIs: The OWASP API Security Top Ten
Christian Wenz
 23:47
23:47Lessons learned from observing a billion API requests
Pratim Bhosale
 58:19
58:19Typed Security: Preventing Vulnerabilities By Design
Michael Koppmann
 24:01
24:01What The Hack is Web App Sec?
Jackie
 29:34
29:34You can’t hack what you can’t see
Reto Kaeser
 44:30
44:30Securing Your Web Application Pipeline From Intruders
Milecia McGregor
Related Articles
View all articles



From learning to earning
Jobs that call for the skills explored in this talk.

Code Healers LLC
Hinesville, United States of America
Remote
€40-50K
Intermediate
Senior
PHP
.NET
React
+2


aXite Security Tools
Amsterdam, Netherlands
Node.js
Angular
JavaScript



LinkiT
The Hague, Netherlands
Linux
Scripting (Bash/Python/Go/Ruby)

Devoteam
IIS
Linux
ServiceNow
Google Cloud Platform
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
+1

