Clemens Vasters
What is a Message Queue and when and why would I use it?
#1about 5 minutes
The history and ubiquity of queues in daily life
Real-world examples like postal services, registration lines, and traffic illustrate the fundamental principles of queuing for managing shared resources.
#2about 11 minutes
How queues already power modern computing systems
Your computer's operating system and network stack rely on multiple hidden queues for CPU scheduling, thread pools, and handling network requests.
#3about 5 minutes
Defining a queue as a fundamental data structure
A queue is a first-in, first-out (FIFO) data structure where taking an item removes it, providing exclusive access and an observable length.
#4about 3 minutes
What a message queue is and how it ensures reliability
A message queue uses a durable broker to accept, store, and manage the lifecycle of each message, guaranteeing delivery even if a consumer crashes.
#5about 1 minute
Why Apache Kafka is not a message queue
Apache Kafka functions as an event stream and lacks key queue features like individual message lifecycle management and exclusive consumer acquisition.
#6about 5 minutes
Understanding the structure of a message as an envelope
A message consists of a payload (the data) wrapped in an envelope with metadata that guides its transport and processing without inspecting the content.
#7about 6 minutes
Exploring real-world use cases for message queues
Message queues are critical in industries like finance, industrial automation, and connected vehicles, and can act as secure bridges between isolated networks.
#8about 1 minute
The competing consumers pattern for load balancing
The competing consumers pattern allows multiple worker processes to pull jobs from a single queue, with the queue ensuring each job is assigned exclusively.
#9about 2 minutes
Using queues for load leveling to handle request bursts
Queues act as a buffer to absorb sudden spikes in traffic, preventing system overload and enabling back-end services to process work at a steady pace.
#10about 2 minutes
Handling message failures with dead-letter queues
A dead-letter queue (DLQ) is a built-in error handling mechanism that automatically collects messages that fail processing or expire.
#11about 2 minutes
An overview of the messaging and eventing ecosystem
The messaging landscape includes different broker types like queue brokers, event stream brokers, and event routers, each suited for different use cases.
#12about 1 minute
The claim check pattern for handling large files
The claim check pattern is the recommended approach for large files, where the file is stored separately and a reference to it is passed through the queue.
Related jobs
Jobs that call for the skills explored in this talk.
envelio
Köln, Germany
Remote
Senior
Python
Software Architecture
Matching moments

01:36 MIN
Understanding the trade-offs of using message queues
The Lifehacker's Guide to Software Architecture

04:17 MIN
The hidden complexity of event-driven architectures
Is your backend a hodgepodge of queues, event stores and cron jobs? Durable Execution to the Rescue.
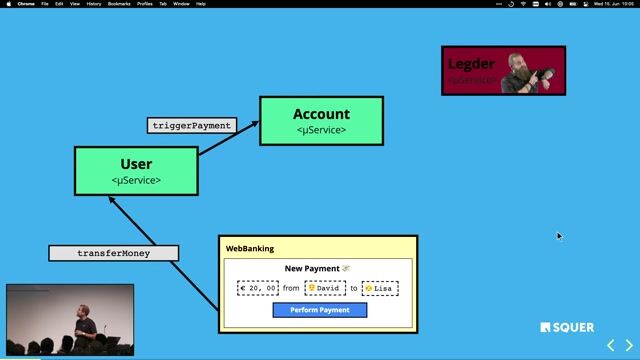
04:11 MIN
Decoupling services with asynchronous message queues
The Rise of Reactive Microservices

03:38 MIN
Answering audience questions on serverless architecture
From 0 to 1.000.000: How to build a serverless raffle service for hyperscale
04:38 MIN
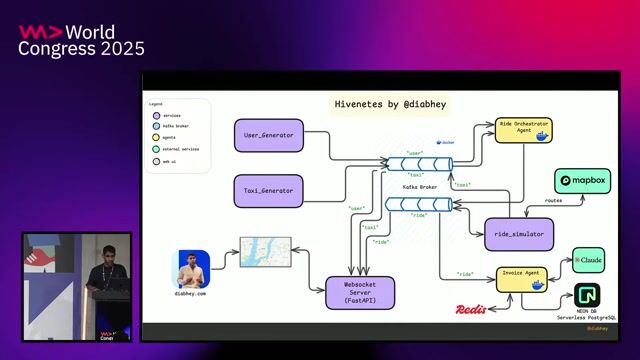
Comparing event-driven and message-driven communication
Event Messaging and Streaming with Apache Pulsar
03:59 MIN
The system design of the event-driven architecture
Event-Driven Architecture: Breaking Conversational Barriers with Distributed AI Agents

22:41 MIN
Answering questions on Kafka use cases, careers, and learning
Let's Get Started With Apache Kafka® for Python Developers

04:23 MIN
A traditional approach to streaming with Kafka and Debezium
Python-Based Data Streaming Pipelines Within Minutes
Featured Partners
Related Videos
 43:27
43:27CQRS and Event Sourcing without the pixie dust
Allard Buijze
 46:24
46:24The Rise of Reactive Microservices
David Leitner
 45:48
45:48Kafka Streams Microservices
Denis Washington & Olli Salonen
 57:38
57:38Are you done yet? Mastering long-running processes in modern architectures
Bernd Ruecker
 28:12
28:12Is reactive the new black? Imperative vs. reactive programming with Quarkus
Tatiana Chervova
 24:22
24:22Database Magic behind 40 Million operations/s
Jürgen Pilz
 52:15
52:15Practical Change Data Streaming Use Cases With Debezium And Quarkus
Alex Soto
 50:06
50:06Single Server, Global Reach: Running a Worldwide Marketplace on Bare Metal in a Cloud-Dominated World
Jens Happe
Related Articles
View all articles



From learning to earning
Jobs that call for the skills explored in this talk.


Zühlke Gruppe
Stuttgart, Germany
Remote
Azure
DevOps
Python
Jenkins
+2


Michael Page International (Deutschland) GmbH
Frankfurt am Main, Germany
Azure
Terraform
Kubernetes

Kramer & Crew
Köln, Germany
Remote
Azure
Powershell
SharePoint
Microsoft Access
+1

Today Experts GmbH
Vienna, Austria
Remote
€61K
UML
XML
GIT
+41



msg systems ag
Berlin, Germany
API
ETL
Azure
SharePoint
Microsoft Dynamics