Markus Kett
In-Memory Computing - The Big Picture
#1about 3 minutes
The critical need for performance in modern applications
Latency is a significant cost for businesses, making high-performance, in-memory computing essential for modern applications.
#2about 2 minutes
Understanding the fundamental speed of in-memory operations
In-memory operations are orders of magnitude faster, measured in microseconds, compared to database access which is measured in milliseconds.
#3about 3 minutes
The core problem of object-relational impedance mismatch
Object-oriented programming languages are inherently incompatible with relational database models, leading to complex and slow data mapping.
#4about 3 minutes
Why NoSQL and mapping layers don't solve the bottleneck
Even with NoSQL databases, the need for data conversion and mapping layers like ORMs persists, creating a significant performance bottleneck.
#5about 3 minutes
Using distributed caches to reduce database load
A distributed cache cluster sits between the application and the database to store frequently accessed data in memory, reducing database load.
#6about 2 minutes
Differentiating in-memory data grids from distributed caches
In-memory data grids extend distributed caches by adding computational capabilities, allowing for distributed processing across the cluster.
#7about 3 minutes
The architecture and limitations of in-memory databases
In-memory databases run the DBMS in memory but often on a separate cluster, which still introduces network latency and requires data mapping.
#8about 4 minutes
A new paradigm: Database-less processing and system prevalence
The system prevalence architecture keeps the entire application state as an object graph in memory, leveraging native language APIs for ultra-fast queries.
#9about 3 minutes
Simplifying architecture and costs with Eclipse Store
Eclipse Store provides a persistence engine that stores the in-memory object graph directly to cloud blob storage, eliminating database clusters and reducing costs.
Related jobs
Jobs that call for the skills explored in this talk.
WALTER GROUP
Wiener Neudorf, Austria
Junior
Intermediate
Java
Solution Architecture
+1
msg
Ismaning, Germany
Intermediate
Senior
Data analysis
Cloud (AWS/Google/Azure)
Sopra Steria Custom Software Solutions GmbH
München, Germany
€78-100K
Senior
Java
JavaScript
+3
Matching moments

02:46 MIN
Using Java's native power for high-speed data processing
Databaseless Data Processing - High-Performance for Cloud-Native Apps and AI
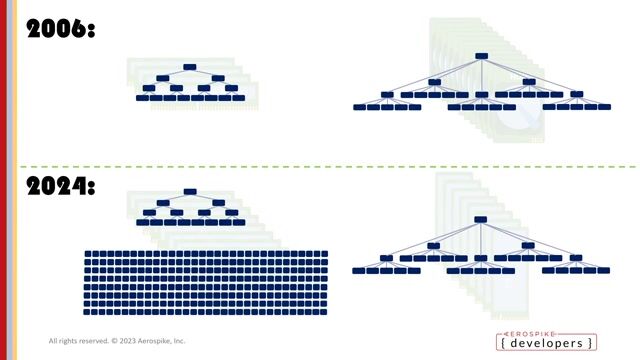
04:20 MIN
An alternative architecture with the index in RAM
Leveraging Moore’s Law: Optimising Database Performance

04:22 MIN
The challenge of real-time data in modern applications
Build ultra-fast In-Memory Database Apps and Microservices with Java
04:10 MIN
Achieving speed and efficiency without caching
Leveraging Moore’s Law: Optimising Database Performance
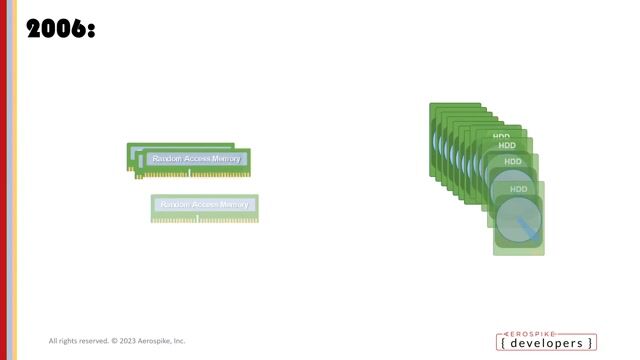
07:20 MIN
Traditional database architecture and its reliance on caching
Leveraging Moore’s Law: Optimising Database Performance
09:31 MIN
How an in-memory caching layer enables massive scale
Single Server, Global Reach: Running a Worldwide Marketplace on Bare Metal in a Cloud-Dominated World
07:33 MIN
Answering questions on Cube's architecture and use cases
Making Data Warehouses fast. A developer's story.

03:43 MIN
Q&A on implementation details and technology choices
Challenges for omnichannel applications at ALDI: Data distribution and offline capabilities
Featured Partners
Related Videos
 44:05
44:05Build ultra-fast In-Memory Database Apps and Microservices with Java
Markus Kett
 24:22
24:22Database Magic behind 40 Million operations/s
Jürgen Pilz
 28:20
28:20Building Real-Time AI/ML Agents with Distributed Data using Apache Cassandra and Astra DB
Dieter Flick
 30:21
30:21Databaseless Data Processing - High-Performance for Cloud-Native Apps and AI
Markus Kett
 30:34
30:34How building an industry DBMS differs from building a research one
Markus Dreseler
 22:32
22:32Swapping Low Latency Data Storage Under High Load
George Asafev
 28:12
28:12Scaling: from 0 to 20 million users
Josip Stuhli
 44:37
44:37Advanced Caching Patterns used by 2000 microservices
Natan Silnitsky
Related Articles
View all articles



From learning to earning
Jobs that call for the skills explored in this talk.

Smart Future Campus GmbH
Dresden, Germany
ETL
JSON
Azure
NoSQL
Scrum
+1

Smart Future Campus GmbH
Bernau bei Berlin, Germany
ETL
JSON
Azure
NoSQL
Data analysis

März Internetwork Services AG
Berlin, Germany
Azure
VMware
Amazon Web Services (AWS)

Smart Future Campus GmbH
Hameln, Germany
ETL
JSON
Azure
NoSQL
Scrum
+1


Integrated Worlds Gmbh
Holzgerlingen, Germany
Remote
Intermediate
Azure
Spark
Routing
Tableau
+4


Smart Future Campus GmbH
Soest, Germany
ETL
JSON
Azure
NoSQL
Scrum
+1
