Wei Hu
Fault Tolerance and Consistency at Scale: Harnessing the Power of Distributed SQL Databases
#1about 3 minutes
Understanding the fundamentals of distributed SQL databases
Distributed SQL databases store data across multiple locations while appearing as a single logical database to the application, addressing needs for fault tolerance, data sovereignty, and scalability.
#2about 2 minutes
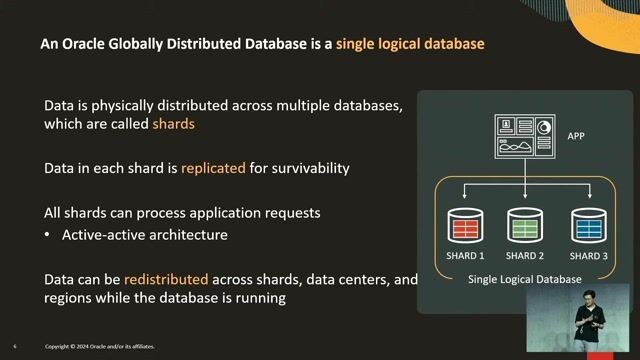
How distributed databases abstract complexity from applications
Applications interact with a single logical database, which automatically routes single-shard requests directly and federates multi-shard requests to maintain transactional consistency.
#3about 2 minutes
Solving data sovereignty requirements without application changes
A distributed database can enforce data residency rules, like storing a country's citizen data locally, while still allowing global processing without requiring application rewrites.
#4about 1 minute
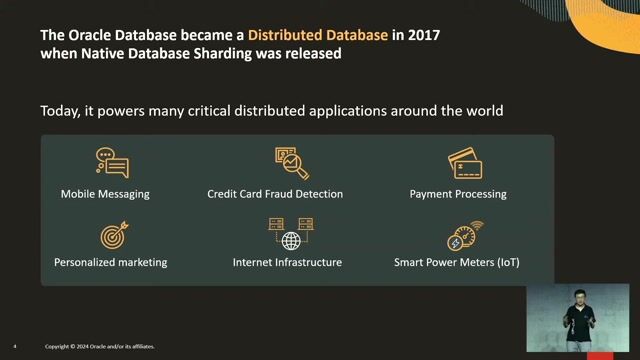
Achieving massive scalability and high fault tolerance
Use cases demonstrate how distributed databases support millions of transactions per second and provide fast, automatic failover with zero data loss for critical systems.
#5about 2 minutes
The architectural advantage of a SQL-native design
Databases architected for SQL from the ground up offer better performance and consistency compared to systems that layer a SQL interface on top of a NoSQL engine.
#6about 2 minutes
Optimizing performance by managing network latency costs
The inherent cost of network latency in distributed systems can be minimized by designing for data locality and reducing the amount of data sent between nodes.
#7about 5 minutes
Choosing the right data distribution method for your workload
Various data distribution methods like value-based, system-managed hashing, composite, and user-defined sharding allow you to tailor data placement to your application's access patterns.
#8about 4 minutes
Handling network failures with adaptive replication strategies
Raft-based replication provides fast, zero-data-loss failover, while adaptive synchronous and asynchronous modes help applications tolerate flaky, real-world network conditions.
#9about 2 minutes
Deploying across multi-cloud to avoid vendor lock-in
A distributed database can span multiple cloud providers and on-premises data centers, allowing workloads to be shifted dynamically to avoid vendor lock-in and optimize costs.
#10about 3 minutes
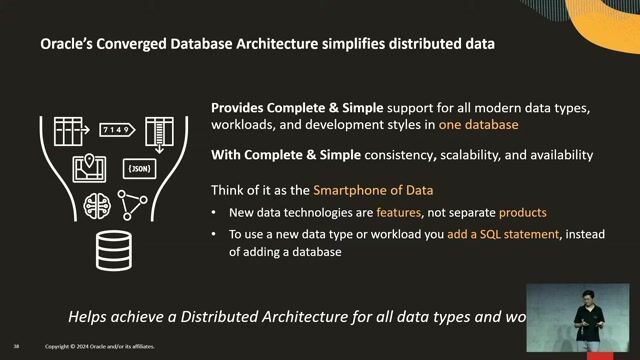
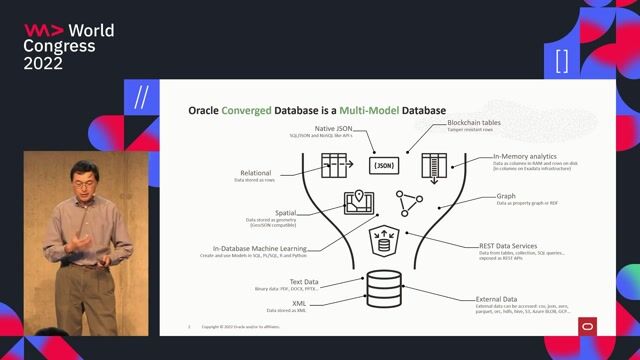
The benefits of a converged database architecture
A converged database supports multiple data types and workloads in a single system, simplifying development and management compared to using many specialized databases.
#11about 1 minute
Key design patterns for distributed database applications
Effective application design involves selecting the right data distribution, co-locating related data, using duplicated tables for common data, and minimizing cross-shard transactions.
#12about 2 minutes
How to evaluate and choose a distributed SQL database
When selecting a distributed database, consider the completeness of its SQL implementation, its replication and deployment options, and whether it offers a converged architecture.
Related jobs
Jobs that call for the skills explored in this talk.
Matching moments

03:15 MIN
The evolution from key-value stores to distributed SQL
Fault Tolerance and Consistency at Scale: Harnessing the Power of Distributed SQL Databases
01:31 MIN
Key features of a modern distributed SQL database
Fault Tolerance and Consistency at Scale: Harnessing the Power of Distributed SQL Databases
01:24 MIN
Understanding the primary use cases for distributed databases
Fault Tolerance and Consistency at Scale: Harnessing the Power of Distributed SQL Databases
03:09 MIN
How a distributed database works under the hood
Fault Tolerance and Consistency at Scale: Harnessing the Power of Distributed SQL Databases
06:12 MIN
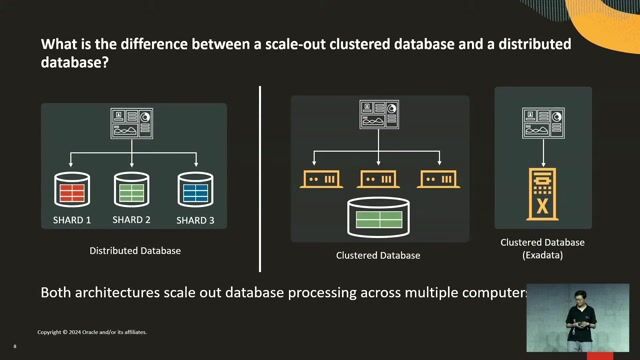
Choosing between distributed and clustered database architectures
Fault Tolerance and Consistency at Scale: Harnessing the Power of Distributed SQL Databases
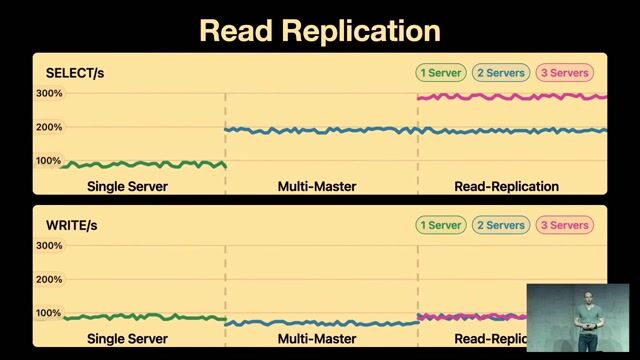
04:48 MIN
The power and complexity of database sharding
Scaling Databases

04:17 MIN
Navigating the CAP theorem in distributed systems
Leveraging Real time data in FSIs

04:58 MIN
Optimizing performance with advanced data distribution methods
Fault Tolerance and Consistency at Scale: Harnessing the Power of Distributed SQL Databases
Featured Partners
Related Videos
 32:46
32:46Fault Tolerance and Consistency at Scale: Harnessing the Power of Distributed SQL Databases
Wei Hu
 21:09
21:09Scaling Databases
Tobias Petry
 26:08
26:08Durable Execution: A Revolutionary Abstraction for Building Resilient Applications
Maxim Fateev
 29:27
29:27Crypto-secure Data Management with In-Database Blockchain
Wei Hu
 29:30
29:30Kubernetes and Microservices with Multi-Model Databases
Wei Hu
 30:34
30:34How building an industry DBMS differs from building a research one
Markus Dreseler
 24:22
24:22Database Magic behind 40 Million operations/s
Jürgen Pilz
 46:58
46:58Distributed search under the hood
Alexander Reelsen
Related Articles
View all articles

.gif?w=240&auto=compress,format)

From learning to earning
Jobs that call for the skills explored in this talk.

Optimadata B.V.
Naarden, Netherlands
Remote
€3-5K
MariaDB
MongoDB
Microsoft SQL Server
+1



Databricks
Amsterdam, Netherlands
Senior
C++
ETL
Java
Spark
Hadoop
+3




DP World
Stanford-le-Hope, United Kingdom
Senior
Azure
T-SQL
PostgreSQL
Powershell
Data analysis
+1
