Wei Hu
Fault Tolerance and Consistency at Scale: Harnessing the Power of Distributed SQL Databases
#1about 3 minutes
The evolution from key-value stores to distributed SQL
Modern distributed systems require strong consistency and a powerful query language, leading to the development of distributed SQL databases.
#2about 1 minute
Understanding the primary use cases for distributed databases
Distributed databases primarily solve for massive internet-scale workloads and help organizations comply with data sovereignty regulations.
#3about 3 minutes
How a distributed database works under the hood
A distributed database presents a single logical view to applications while physically partitioning data into replicated, independently operating shards.
#4about 6 minutes
Choosing between distributed and clustered database architectures
Clustered databases offer the lowest latency within a data center, while distributed databases provide massive geographical scale at the cost of network latency.
#5about 4 minutes
Using database sharding to meet data sovereignty laws
A global bank implemented data sovereignty for India by sharding local customer data into a dedicated region without changing its core applications.
#6about 3 minutes
Supporting hyperscale workloads with a single database
The BlueKai platform simplified its architecture and improved performance by migrating a complex, multi-database system to a single Oracle distributed database.
#7about 5 minutes
Optimizing performance with advanced data distribution methods
Flexible data distribution methods like composite, directory-based, and duplicated tables are crucial for minimizing latency and handling data skew.
#8about 2 minutes
Building resilient systems with modern replication protocols
Using adaptive replication and the Raft consensus protocol provides extreme survivability and fast, automatic failover with zero data loss.
#9about 2 minutes
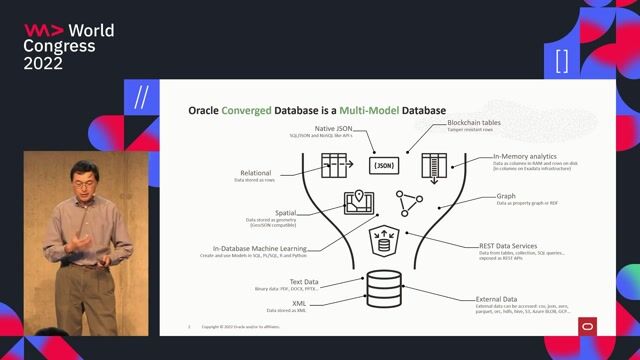
The converged database model for modern applications
A converged database supports multiple data types and workloads in a single system, simplifying development and deployment across multi-cloud and on-premise environments.
#10about 2 minutes
Key features of a modern distributed SQL database
A fully-featured distributed database combines flexible data distribution, replication, and deployment methods within a converged architecture for maximum power.
Related jobs
Jobs that call for the skills explored in this talk.
ROSEN Technology and Research Center GmbH
Osnabrück, Germany
Senior
TypeScript
React
+3
Matching moments

03:03 MIN
Understanding the fundamentals of distributed SQL databases
Fault Tolerance and Consistency at Scale: Harnessing the Power of Distributed SQL Databases

01:32 MIN
How distributed databases abstract complexity from applications
Fault Tolerance and Consistency at Scale: Harnessing the Power of Distributed SQL Databases

01:15 MIN
Achieving massive scalability and high fault tolerance
Fault Tolerance and Consistency at Scale: Harnessing the Power of Distributed SQL Databases

02:00 MIN
How to evaluate and choose a distributed SQL database
Fault Tolerance and Consistency at Scale: Harnessing the Power of Distributed SQL Databases

01:57 MIN
Solving data sovereignty requirements without application changes
Fault Tolerance and Consistency at Scale: Harnessing the Power of Distributed SQL Databases

02:14 MIN
Deploying across multi-cloud to avoid vendor lock-in
Fault Tolerance and Consistency at Scale: Harnessing the Power of Distributed SQL Databases

04:17 MIN
Navigating the CAP theorem in distributed systems
Leveraging Real time data in FSIs
04:48 MIN
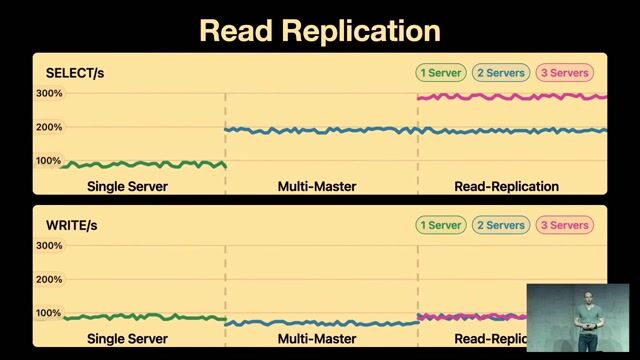
The power and complexity of database sharding
Scaling Databases
Featured Partners
Related Videos
 28:41
28:41Fault Tolerance and Consistency at Scale: Harnessing the Power of Distributed SQL Databases
Wei Hu
 21:09
21:09Scaling Databases
Tobias Petry
 29:27
29:27Crypto-secure Data Management with In-Database Blockchain
Wei Hu
 26:08
26:08Durable Execution: A Revolutionary Abstraction for Building Resilient Applications
Maxim Fateev
 30:34
30:34How building an industry DBMS differs from building a research one
Markus Dreseler
 29:30
29:30Kubernetes and Microservices with Multi-Model Databases
Wei Hu
 24:22
24:22Database Magic behind 40 Million operations/s
Jürgen Pilz
 22:32
22:32Swapping Low Latency Data Storage Under High Load
George Asafev
Related Articles
View all articles

.gif?w=240&auto=compress,format)

From learning to earning
Jobs that call for the skills explored in this talk.

Databricks
Amsterdam, Netherlands
Senior
C++
ETL
Java
Spark
Hadoop
+3

Optimadata B.V.
Naarden, Netherlands
Remote
€3-5K
MariaDB
MongoDB
Microsoft SQL Server
+1


DP World
Stanford-le-Hope, United Kingdom
Senior
Azure
T-SQL
PostgreSQL
Powershell
Data analysis
+1



Oracle
Charing Cross, United Kingdom
Remote
Senior
Java
Azure
Linux
MySQL
+8

Liebherr-International Deutschland GmbH
Ulm, Germany
Kafka
Docker
Kubernetes

Westhouse Consulting GmbH
Frankfurt am Main, Germany
API
SAP HANA
Data analysis