Tillman Radmer & Fabian Hüger & Nico Schmidt
Uncertainty Estimation of Neural Networks
#1about 5 minutes
Understanding uncertainty through rare events in driving
Neural networks are more uncertain in rare situations like unusual vehicles on the road because these events are underrepresented in training data.
#2about 3 minutes
Differentiating aleatoric and epistemic uncertainty
Uncertainty is classified into two types: aleatoric (data noise, like blurry edges) and epistemic (model knowledge gaps), which can be reduced with more data.
#3about 3 minutes
Why classification scores are unreliable uncertainty metrics
Neural network confidence scores are often miscalibrated, showing overconfidence at high scores and underconfidence at low scores, making them poor predictors of true accuracy.
#4about 2 minutes
Using a simple alert system to predict model failure
The alert system approach uses a second, simpler model trained specifically to predict when the primary neural network is likely to fail on a given input.
#5about 15 minutes
Using Monte Carlo dropout and student networks for estimation
The Monte Carlo dropout method estimates uncertainty by sampling predictions, and its performance can be accelerated by training a smaller student network to mimic this behavior.
#6about 14 minutes
Applying uncertainty for active learning and corner case detection
An active learning framework uses uncertainty scores to intelligently select the most informative data (corner cases) from vehicle sensors for labeling and retraining models.
#7about 4 minutes
Challenges in uncertainty-based data selection strategies
Key challenges for active learning include determining the right amount of data to select, evaluating performance on corner cases, and avoiding model-specific data collection bias.
#8about 7 minutes
Addressing AI safety and insufficient generalization
Deep neural networks in autonomous systems pose safety risks due to insufficient generalization, unreliable confidence, and brittleness to unseen data conditions.
#9about 8 minutes
Building a safety argumentation framework for AI systems
A safety argumentation process involves identifying DNN-specific concerns, applying mitigation measures like uncertainty monitoring, and providing evidence through an iterative, model-driven development cycle.
Related jobs
Jobs that call for the skills explored in this talk.
CARIAD
Berlin, Germany
Junior
Intermediate
Python
C++
+1
Wilken GmbH
Ulm, Germany
Senior
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Kubernetes
+1
Matching moments

03:37 MIN
Advancing automated driving with AI and neural networks
Software is the New Fuel, AI the New Horsepower - Pioneering New Paths at Mercedes-Benz

00:43 MIN
Finding the unknown unknowns in autonomous driving
Finding the unknown unknowns: intelligent data collection for autonomous driving development

02:51 MIN
Understanding the long-tail problem in driving scenarios
Finding the unknown unknowns: intelligent data collection for autonomous driving development

06:13 MIN
Skills and challenges of working with automotive AI
Developing an AI.SDK

02:59 MIN
Navigating the uncertainty of building AI products
The End of Software as we know it
05:14 MIN
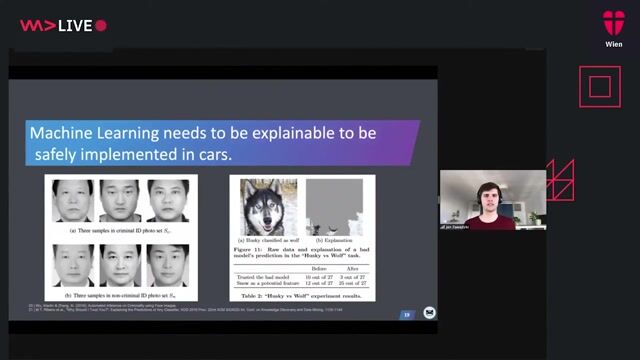
Challenge three: Ensuring machine learning models are robust
How Machine Learning is turning the Automotive Industry upside down
02:50 MIN
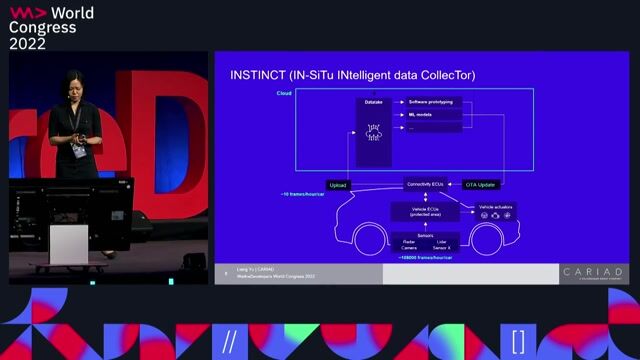
How INSTINCT software identifies valuable data
Finding the unknown unknowns: intelligent data collection for autonomous driving development
05:03 MIN
Q&A on ethics, model deployment, and regional data
Finding the unknown unknowns: intelligent data collection for autonomous driving development
Featured Partners
Related Videos
 35:16
35:16How AI Models Get Smarter
Ankit Patel
 19:24
19:24Finding the unknown unknowns: intelligent data collection for autonomous driving development
Liang Yu
 38:12
38:12Developing an AI.SDK
Daniel Graff & Andreas Wittmann
 48:01
48:01What non-automotive Machine Learning projects can learn from automotive Machine Learning projects
Jan Zawadzki
 52:10
52:10Intelligent Data Selection for Continual Learning of AI Functions
Nico Schmidt
 28:05
28:05A walkthrough on Responsible AI Frameworks and Case Studies
Toju Duke
 42:18
42:18On the straight and narrow path - How to get cars to drive themselves using reinforcement learning and trajectory optimization
Francis Powlesland & Elena Kotljarova
 30:57
30:57Enhancing AI-based Robotics with Simulation Workflows
Teresa Conceicao
Related Articles
View all articles



From learning to earning
Jobs that call for the skills explored in this talk.

Imec
Azure
Python
PyTorch
TensorFlow
Computer Vision
+1

BMW AG
München, Germany
Python
Computer Vision
Machine Learning
Amazon Web Services (AWS)

Everllence SE
Augsburg, Germany
C++
Python
Matlab
Machine Learning

BMW AG
München, Germany
Python
PyTorch
TensorFlow
Machine Learning
Natural Language Processing


RIB Deutschland GmbH
Stuttgart, Germany
Python
Machine Learning

DKV Euro Service GmbH + Co. KG
Ratingen, Germany
Remote
Intermediate
Azure
Python
Docker
Terraform
+3

Neural Concept
Großmehring, Germany
Fluid
Python
Machine Learning

Bundesanstalt für Arbeitsschutz und Arbeitsmedizin
Dresden, Germany
GIT
Python
Docker
PyTorch
TensorFlow
+1